Meta Description: Find out the number of kW generator that you require to keep your whole house running. Comprehensive solutions to determine the right size generator, power needs, cost, and mounting advice on generators in 2025.

During an incident of power outages, the appropriate-sized generator can spell the difference between the ability to continue with your usual lifestyle and the inability to have the bare necessities. To make a sound investment decision, you need to know the power needs and number of kilowatts (kW) that your generator must be able to yield in order to effectively run the house. This guide will give you all the information on how to size your home generator/generator performance and get the information you need on how to calculate your power requirement, what type of generator suits your needs and what capacity the generator must have.
Understanding Generator Power Ratings and Electrical Basics
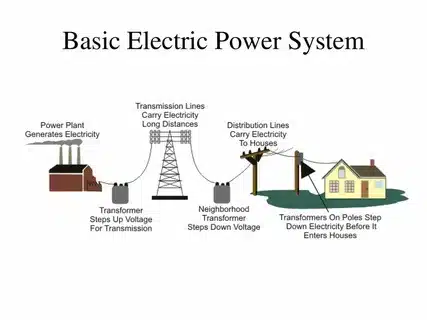
Generators and the appliances in your house will use the watts (or kilowatts as 1,000 watts) to indicate the amount of electricity they produce or consume. The key principles of basic electrical terminologies will help you understand how much power is required when choosing the most appropriate size of generator in your home.
Quite often various power is discussed in terms of watt (W): 1,000 watts = 1 kilowatt (kW). Residential generators have most sizes, with a variety between 5 kW and 50 kW although their usage varies. Power rating shows the maximum electrical load that the generator can sustain, without overloading.
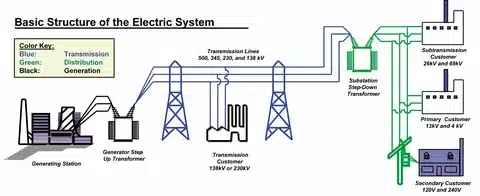
Two important terms that must be known as running watts and starting watts. Running watts are the power required to run appliances habitually, and starting watts (sometimes referred to as surge watts) are the additional power a motor, or compressor, needs when coming on-line. Most appliances have much more starting 5kilowatt (kw). The maximum power they use than the running continuous power 5kilowatt (kw). The effect of this is that you cannot base your generator sizing calculations solely on the starting wattage and running continuous kilowatt (kw) in order to avoid overloading .
Essential vs. Non-Essential Electrical Loads in Your Home
Before determining generator size, categorize your home’s electrical loads into essential and non-essential items. The critical loads are usually refrigeration, heating/ cooling systems, lighting, medical devices and the security systems. Loads such as additional appliances, entertainment systems and convenience items may be considered as non-essential.
In a normal 2 bed house, with minimal load on it (some lights, fridge and heating), may need 5000 – 7000 Watts. This baseline is useful in setting minimum requirements of eight generators about basic comforts and safety.
Making a priority list will allow you to realize what you would like to have priority power over or just stay at the level of what you feel that you absolutely would need. This decision significantly impacts the generator size and cost you’ll need to consider.
Small Home Generator Requirements (Under 1,500 sq ft)

In small houses less than 1,500 square foot, requirements are usually more manageable in terms of generators. It is possible to save with a smaller generator of 10-15 kW when a properly designed installation can address basic needs such as a sump pump depending on the selected appliances and systems in the household.
The main questions to answer when considering small homes are the form of heating available (gas or electric), how many major appliances will be there, and what level of comfort will be expected when there is an outage. Applications using electric heating systems are highly power intensive compared with those using gas and this may move requirements to the upper end of this spectrum.
Even most small houses can sustain basic services by watching the load carefully, so it is possible to plan the use of large appliances instead of operating things all at once. This strategy may be applied to maximize the functioning of generators and fuel consumption.
Medium Home Generator Requirements (1,500-3,000 sq ft)

The minimum size needed can be satisfied with a 15,000-watt unit that serves the necessities in a 2,000-square-foot home. Medium sized houses normally need generators of between 15-25 kW to support critical systems and only bigger generators can be used to provide back up to the entire house.
These houses tend to have more complex electric system, more HVAC zones, bigger appliances and more advanced lighting networks. The additional square feet leads to additional circuits and even electrical consumption, including air conditioners .
Medium-sized homes that want to cover all the backup power, as well as non-essential loads, can easily have a generator requirement up to 22-30 kW. This of size is flexible to operate the maximum wattage of majority of systems required in the households without meticulous handling of the load, or organization of appliances.
Large Home Generator Requirements (Over 3,000 sq ft)

Generators: Luxury homes that measure more than 3,000 square feet usually have to have fairly big generators (25-50 KW or higher) based on luxury features and electrical systems. These houses often comprise of more than one HVAC systems, massive lighting, heavy appliances and special machines.
In this situation, you’d probably want at least a 35kW whole-home generator. Generators in this high end capacity are needed to keep such large homes with high electricity demands, two or more air conditioners, electric heating systems and other luxurious amenities at a normal functioning capacity.
Imagine that the home may be large and with a pool, hot tub, or a workshop or other such high power using facility that a great determinant of much generator sizing. Electrical systems and loads get more complex and this makes professional assessment more imperative to the homes in this category.
Calculating Your Home’s Total Electrical Load

Correct load calculation is to ensure that you count all the electrical appliances that you wish to operate during an outage period and also calculate its running and starting power demands. Begin by making a list of all the appliances, lighting, systems you regard as your necessities.
Running wattage (R) + Run time (R x 3) = total wattage required This equation is useful to cover those appliances that demand higher power when it starts. Even so, the precise multiplier differs depending on the type of appliance and consulting its specifications gives more precise calculation.

Experienced electricians employ professional software and measuring tools to calculate the real load of the electrical system, taking into account such aspects as diversity (all loads would not run at the same time; future capacity requirements). This approach ensures your generator investment adequately serves your home’s requirements during generator power outages .
Major Appliances and Their Power Requirements
Knowledge about power consumption of each appliance will contribute to the formation of viable calculations of the loads. Most refrigerators need 600-800 watts running and can also have starting requirements of 2,000+ watts. Such systems as a whole range of central air conditioning systems may be 3,000-7,000 watts in wattage, and their sizes are differing.
Electric water heaters incur a 3,000-5,000 watts of electricity consumption and during the course of use, tankless ones probably need even more electricity. Systems are wildly different: the electric furnaces may draw up to 10,000-25,000 watts where the gas furnace with the blower working on electric power usually draws up to 600-1,200 watts.
Home appliances put extra load when they are used at the same time. Make sudden demands due to short term spiking of high power loads on the electric supply: Some common electric loads that can demand high levels of power when in peak usage include dishwashers (1,800 watts), microwave ovens (1,000-1,500 watts) and electric ranges (3,000-5,000 watts).
Portable vs. Standby Generator Sizing Differences
If you want a portable generator that can power a whole house, you’re looking for at least a 10,000 watt generator or a likely more in the 15,000 watt portable generator range. Portable generators can be flexible and supplies less power compared to standby as a rule.
Portable generators have to be manually connected using transfer switches or extension cords and thus have limited applicability in providing backup to the entire home. They’re excellent for essential loads but may require load management to operate effectively.
Standby generators automatically activate during outages and can be sized more precisely for your home’s complete electrical system. They are more convenient and will be able to deliver a larger load, but need the special installation and it should be more expensive initially.
Fuel Type Considerations: Natural Gas vs. Propane vs. Diesel

The type of fuel influences the selection of size as well as performance of the generators. Natural gas generators can have unlimited run time (when connected to utility line), with the ability of providing good power output and is suitable to be used in the standby use in places where there is availability of natural gas service.
Propane generators have the benefits of being clean burning, and do not require refrigeration, and short storage life as natural gas or gasoline units. During prolonged outages, propane tanks have to be checked and refilled, which interferes with the operational planning.
Diesel generators are highly efficient in fuel consumption and performance delivery but they necessitate fuel warehousing and also, they might not be friendly to the residential premises because of sound and emission controls. They’re more common in commercial applications or rural settings.
Professional Load Calculation vs. DIY Assessment Methods
Accuracy offered by professional load calculations is essential in facilitating the sizing of generators. Licensed electricians apply specialized equipment to determine real electrical use, areas of inefficiency, and future electrical demands or alterations in the home.
Home generator suppliers local to you will be in a position to advise you best in regard to the whole-house generator sizing. The professional evaluation takes into account such aspects as starting schemes, diversity of loads, and what constitutes a correct size generator electrical code considerations that could be overlooked in DIY estimations.
Do-it-yourself evaluation of the online calculator or appliance tags can help in crude approximations that are enough as a starting point. But professional evaluation is important with major generator purchases to make sure that it is sized properly and will not cost enormous sums of money in the long run of making mistakes.
Cost Factors: Generator Size vs. Installation Investment
The price of generators is also very high by the size and features. Simple 10-15 kW systems might be priced at between $3,000 and $6,000, whereas 25-35 kW systems could set people back 8000-15000 dollars or more, not to mention the cost of the actual installation.
Installation prices depend upon what amount of electrical work is essential, fuel connections, authorization, and readying the location. Depending on the complexity and local codes, the cost of professional installation of standby generators averages between 3000 to 8000 dollars, on top of the pool-related project cost.
The long-term operating expenses such as fuel consumption, maintenance needs and possible repair of the machine should also be considered. Properly sized generator has a higher efficiency in comparison to oversized generators, and could save fuel in the future by serving as a backup power source appropriate generator size.
Installation Requirements and Electrical Considerations
Installation of a generator is much electrical work such as transfer switch, load center and possible electrical panel upgrade. Local codes usually insist on professional installation and electrical permits of standby generators.
There are a number of placement requirements which involve the clearance in windows, air intakes, and a property line. It is possible to find that noise codes can influence location choices, especially where there are heavily populated residential states. Other installation considerations include more concrete pad, connectivity of fuel and weatherproofing.
The transfer switches ensure that back feeding of electricity to the utility lines does not occur, which safeguards the utility workers and eliminates damage to such equipment essential appliances. Automatic transfer switches facilitate smooth switching of power although they are more expensive than manual switches that will need the intervention of an operator power failure.
Conclusion
How many kW of a generator is appropriate in your house depends on taking into consideration the kind of electrical loads that you have in your house, what kind of lifestyle you want to have, and also what kind of budget do you have. Although simple essential needs may be satisfied by the use of 10-15 kW generators, a whole house generator of 20-35 kW or larger is a typical requirement needed to supply all the needs of the home, based depending on the size and specific electrical systems of the home. Prosperous evaluation leads to the best size for uninterrupted power ; thus, you can invest in a generator that offers backup power to your home that may last many years larger generator.

