Meta Description: Get to know the fundamental methods of conducting circuit breaker tests such as primary injection, secondary injection and timing. Find out how, when and why to carry out a proper electrical safety test.
Circuit breakers are the unsung workhorses of electric systems as they stand in between valuable equipment, and human life alike as they prevent electrical flow in the event of hazardous conditions. Nevertheless, like every protective device, circuit breakers must be regularly tested so that nobody is disappointed to find out they are not useful when they are expected most. This circuit breaker testing guide covers everything there is to know about the importance of circuit breaker testing procedures and how you can know when to do it and why it should be done.
What is Circuit Breaker Testing?

Circuit breaker testing is a methodical procedure of assessing the reliability and the functioning of circuit breakers at different situations of operation. The tests ensure that the breakers will break correctly when a fault occurs to ensure any damage is avoided and put off any potential hazard. Testing the breaker is done by the introduction of controlled electrical signals to simulate as much as possible the conditions of the real world and measuring the response of the breaker.
This is because of professional testing of circuit breakers, which guarantees protection according to manufacturer specification and industry. In absence of appropriate testing, circuit breakers could not operate when needed which could cause damage to equipment and resulting in electrical fires or injuring people.
Why Circuit Breaker Testing is Critical
Safety Protection
The main objective of the testing of circuit breakers is to make sure that human life is secure. Defective breakers may not trip under overload and as a result may cause electrocution, fire or a blast in equipment. Through frequent testing, it is possible to detect a possible breakdown that could be life threatening.
Equipment Protection
Circuit breakers safeguard costly electrical devices against short circuit, overloads and miscellaneous faults by intervening into the situation. Putting these protective devices through testing will make sure that they will work when required and avoid replacing expensive equipment and long periods of time without production.
Regulatory Compliance
Most industries have a need based requirement towards testing circuit breakers to meet their safety guidelines and requirements. Such organizations as IEEE, NEMA, and OSHA have requirements under which maintenance and testing of an electrical system is expected to be implemented.
Operational Reliability
An unanticipated power cut may be very uneconomical to the business. Routine testing also allows to determine aging elements and failure points so that proper maintenance can be undertaken to eliminate unscheduled outages.
When to Perform Circuit Breaker Testing
Initial Installation Testing
Before new circuit breakers are put into service, they ought to be thoroughly tested. This is a commissioning test and checks that the breaker is within specifications and functions properly in the desired application.
Scheduled Maintenance Testing
Routine maintenance should be done as determined by the manufacturers and the industrial eligible guidelines. Normal schedule runs between once a year and every five years depending with the type of breakers and application and the environment within which they operate.
After Fault Conditions
Circuit breakers that have been used under fault conditions are supposed to be tested so that it can verify whether they are in a position to protect the system. Internal damage may be experienced as a result of high-current interruption which might not be evident at a go.
Before Critical Operations
Protective systems may also be verified before critical operations or during scheduled maintenance windows by testing, to add more certainty to the reliability of the systems.
Types of Circuit Breaker Testing
Primary Injection Testing
Primary injection testing uses high primary-circuit-breaker current injected directly into the primary circuit to test the breaker. This test is used to prove the total protection system, to include current transformers, protective relays, and the breaker mechanism itself.
Secondary Injection Testing
Secondary injection testing is the process of applying test signals to the secondary connections of its protective relays leaving that breaker in service. The relay logic and timing are checked with minimal test currents made, and there is no need to remove the breaker out of service.
Distant injection can confirm the relay settings, chronometric qualities and communication signals. Although it is not able to put all the system to test as is done on a primary injection test, it offers good insight on relay performance and can help to detect a lot of possible issues.
Timing Tests
Testing timing The speed of opening and closing of the breaker is measured on timing tests. The tests confirm that the breaker works within acceptable time frames and can detect mechanical faults that may hamper the performance.
Contact timing tests are used to measure the sequence and timing of contact operation ensuring that there is coordination among the phases. Tests enable Trip timing, which ensures that the breaker will open so fast that faults can be cleared before equipment damages.
Insulation Resistance Testing
Insulation resistance test is used to measure resistance of insulation material in the breaker. This test is able to detect moisture entry, trash, or decay that may result in failure of insulation.
Testing is usually conducted with the help of a megohmmeter which applies high DC voltage and measures the current given. The comparison of results is made to manufacturer specifications and to past test results to determine a trend or an emerging problem.
Essential Testing Equipment
High-Current Test Sets
Primary injection testing involves some special equipment with the capability of producing high current in a safe manner. Such test sets normally incorporate current transformers, systems to control test and protection systems to safeguard operators and equipment.
Protective Relay Test Sets
Secondary injection testing applies advanced test gears with the capacity to draw fine test signal and estimate relay reaction. In modern testing sets computer control and automatic test sequences are common.
Timing Test Equipment
The operation of breakers is measured to microsecond accuracy by special timing test equipment. Such devices are capable of recording the timing of contacts, aspects of travel as well as mechanical performance information.
Insulation Testing Equipment
The meghmmeter test sets are high DC voltages used to measure insulation resistance. The use of more modern instruments may have the function of data logging and the ability to automatically repeat a series of tests.
Testing Procedures and Best Practices
Pre-Test Preparation
Prior to conducting any test, safety measures should be observed. This would entail that the breaker is de-energized, safety tags are used and that everybody knows that there is a testing going on.
Check through documentation and earlier test performance to get a baseline performance expectation. Install all required test equipment and ensure that certifications of calibration are up-to-date.
Test Execution
Use set test procedures in a methodical way, by noting all test parameters and outcomes. Always give attention to the safety requirements and never proceed with any other procedure.
Check the test results as it is moving and be ready to halt testing in case of certain abnormal notes. Record any abnormalities or any unforeseen outcomes in preparation of a more elaborated investigation.
Data Analysis
Compare test data to manufacturer reference and industry standards with past performance data. Search for patterns that could show emerging issues or performance decline.
Use timing analysis to make sure that there will be coordination with other system protective devices. Make sure that all test parameters are not out of range.
Common Testing Challenges and Solutions

Access Limitations
Testing may be hard due to limited access to breakers in service. Solution: Schedule testing to test during regular maintenance periods, and provide liaison to the operations staff.
Safety Concerns
Testing high-voltage, high-current poses huge safety threats. Remedy: Apply skilled manpower, correct practices, and acceptable safety gear.
Equipment Limitations
Older breakers might not be adapted in conjunction with contemporary testing gear. Remedy: Apply suitable test procedures and instruments that are suitable to the type of breaker.
Time Constraints
Detailed testing may take a long time. The solution: Visual maintenance should include critical breaker prioritization and effective test procedures where downtime will be reduced.
Interpreting Test Results
Performance Criteria
Tests must be compared with the manufacturer’s specifications, the industry specifications and past measurements. Seek values which are outside the limits of the acceptable or which differ substantially with prior tests.
Trending Analysis
Remarkable results on a track test should be followed over time in order to reveal trends of performances. Slow changes are the ones that signal normal aging, whereas abrupt ones are cause of potential issues.
Failure Analysis
When there are indications by the tests that there are possible problems, test again to be able to isolate the cause. This can entail perform testing on particular parts or features.
Maintenance Based on Test Results
Preventive Maintenance
Preventive maintenance activities should be determined based on test results. This may involve cleaning, lubrication or adjustment of working mechanisms.
Corrective Actions
Upon uncovering issues, through tests, corrective measures need to be put in place. This may include replacement of components, adjustment of settings as well as entire breaker replacement.
Follow-up Testing
Follow up-testing should be done after any maintenance activities to ensure that issues have been solved and that normal performance has been achieved.
Industry Standards and Compliance
IEEE Standards
Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) has published standards of circuit breaker testing such as IEEE C37.09 and IEEE C37.100 series.
NEMA Guidelines
The circuit breaker testing and maintenance is defined in different applications in the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA).
OSHA Requirements
OSHA platform (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) stipulates that the conduct of testing of electrical protective devices must be done regularly at workplaces.
Future Trends in Circuit Breaker Testing
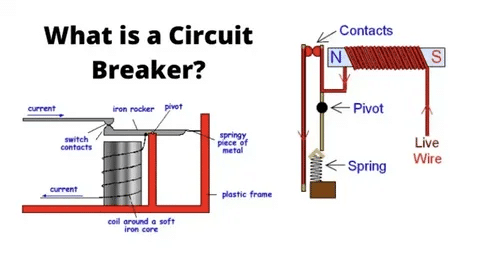
Digital Technology Integration
Circuit breakers have grown increasingly to be integrated with the use of digital technology which allows the remote monitoring and testing of breakers. Having a constant performance data and warning about possible issues in advance can be facilitated through these systems.
Predictive Maintenance
The data on circuit breaker testing were being used to predict failures ahead of time with the help of advanced analytics and machine learning. It is an option that can maximize maintenance plans and minimize the unscheduled failures.
Automated Testing Systems
New automated test systems are under development which may be able to carry out routine testing requiring minimal manual interaction. Testing consistency can be enhanced and safety risks minimized by use of such systems.
Cost Considerations
Testing Costs
Circuit breaker testing involves expenses and provisions of equipment and personnel as well as time down the system. These costs, however, are usually very minimal compared to the possible cost of an equipment breakdown or even a breakdown that was not deemed to occur.
Return on Investment
The use of regular testing offers good returns in the form of avoiding damages to the equipments, reduced downtimes which, and the life span of the equipments. The value of the investment of the testing is normally paid back numerous times over through failures discouraged.
Budget Planning
Come up with a detailed budget in which equipment, personnel and maintenance costs are included. Use the age and criticality of equipment as a part of prioritizing the testing activity.
Conclusion
Testing of circuit breakers is best accomplished through an integrated method which incorporates the right tools, people and workflow. Investment in regular testing and maintenance could assure organizations of the fact that their electrical systems are safe, reliable, and that they comply with the norms of the industry. The price of testing is a drop in the ocean compared to the possible outcome of failed circuit breaker and it should form part of any electrical maintenance program.

