Learn the major distinction between the power generators and the inverter generators. Discover the efficiency, noise level, cost, and the best option that fits your need in our detailed in our 2025 guide.
What Are Power Generators and Inverter Generators?
Both power and inverter generators perform one of the most important tasks, that is, supplying electricity when the grid does not work, however they achieve this goal in completely different ways. The differences between them are important to understand to make a reasonable purchasing choice contingent upon your particular power requirements and financial constrains.
Conventional portable generators work and use a simple mechanical equation in which an alternator is powered by a direct drive from an internal combustion engine like a gasoline powered one. This alternator operates at a fixed rate generally, 3,600 RPM, independent of the electrical load demand. The engine is operated at full throttle 24 hours every day to generate alternating current (AC) power with set frequency of 60 Hz.
Inverter generators do use a more complex 3-step power conversion. The engine is treated to alternating current (AC) then directly converted to direct current (DC) power by means of a rectifier. Lastly, it is an electronic inverter that restores the DC power into clean AC power at controlled voltage and frequency. Under this electronic throttling, the engine will automatically slow or speed up in accordance to power required and thus will have a huge increase in means of efficiency.
Key Differences: Traditional Generators vs Inverter Generators
Engine Operation and Efficiency
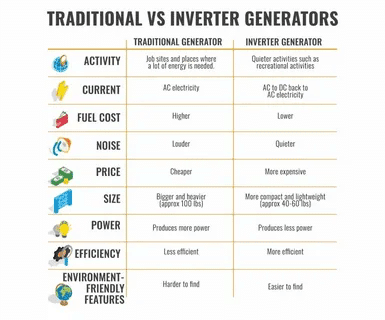
The greatest distinction is the manner in which the two units handle the operation of the engine. Conventional generators also have to keep the engine rotating at full speed with no regard to the load required which translates to full consumption of fuel no matter how many or how few loads you are running.
Inverter generators are using variable engine speed that automatically regulate RPM according to electric demand. Much when it is powering what is termed as light loads, the engine runs slower and consumes less fuel. It increases to hamper demand under heavy loads. This smart throttling has had the capacity to cut fuel consumption by up to 40 percent in comparison to the conventional types of generators and hence the inverter units are far much more economical to be used on a longer basis.
Power Quality and Clean Energy Output
The other important difference between these types of generators is the power quality. Conventional generators supply power naturally with variations in both voltages and frequencies causing what is referred to as dirty power. These surges have the potential to harm delicate electronics such as computer, smartphone, medical equipment and new age appliances that are made with electronic controls.
Inverter generators are clean power, with stable voltage and frequency and very close to utility quality electricity. Electronic inverter technology in providing the power is uniform and has less than 3 percent of total harmonic distortion (THD) which is safe with sensitive electronic devices and medical devices which require a stable source of power.
Noise Levels and Sound Emissions
A noise pollution aspect is also an important factor of concern, particularly in residential purposes or even camping. The conventional generators have a range of 65-75 dB which is fairly like heavy traffic or a garbage disposal with its engine running. This amount of noise may be obstructive to neighbors and prohibit an easy conversation within a 20 feet radius of the unit.
Compared to other common generators, inverter generators are a lot quiet with an average power of 50-60 decibels. Most of them have closed housings, which include sound absorbing materials and adjustable engine speed which further cut down the noise level. This qualifies them to be used during camping, tailgating, or in the residential areas where noise codes can come in to effect.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment vs Long-Term Value

Purchase Price Comparison
The first point of distinction between these two types of generators is being most obvious the initial purchase price. The initial cost of traditional portable generators is much cheaper, with quality 7,500-watt models going at about $800-$1,200. Similar 5,000-7,000 watt inverter generators are around $3,000-$4,500 with a 3-4x mark up.
The sources of this price gap are the complex electronic parts that the inverter technology demands, the electronic inverter, itself, the complex engine management systems, and the high possible production tolerances that allow production of clean power.
Operating Costs and Fuel Efficiency
Long term operating costs speak in another hand. The high level of fuel economy of the inverter generators may lead to high savings in the long run and particularly among those who use the generators regularly or within prolonged periods of time. This reduction of 40 percent goes a long way in terms of saving cost in case of long power cuts or general operation.
To put this in perspective, assume that you use a generator 100 hours a year, and an inverter generator can use 30-40 gallons a year of fuel versus a conventional unit. At today fuel prices, this saves up to 100-150dollars each year so it does pay off in the long run.
Maintenance and Repair Considerations
Traditional generators as a rule provide simpler maintenance and repairing because the construction is less complicated. An automotive service is simple enough to be done by the mechanically minded homeowner, and spare parts are readily available and are economical.
Inverter generators are more complex in nature thus necessitating more specialized service. It is small in size too, which means it is more difficult to replace internal parts or repair the device, sometimes requiring special services. Nevertheless, engine life can be increased by the variable engine speed operation that minimizes wear and tear through the light-load performance.
Performance Comparison: Power Output and Reliability

Starting and Running Watts
It is important to know the differences between the starting and running watts, which applies to both types of generators. Starting watts (surge power) Simply the highest power available at a momentary basis to start motor operated appliances such as refrigerator, air conditioner or power tool. Running watts express the full time power which can be used during repeated operation.
Conventional generators normally have higher starting watt ratings compared to running watt capacity, which qualifies them to start big appliances or motor driven appliances. A 7500 watt conventional generator may supply 9000-10,000 starting watts.
The inverter generators also tend to have a smaller starting margin of watts, a 5,000-watt inverter generator may offer maybe 5,500-6,000 starting watts. This may deteriorate their capability of switching on large appliances or turning on several items at a time.
Runtime and Fuel Capacity
The difference between these types of generator with regard to the runtime capabilities is very high. The traditional generators have large fuel tanks (5-8 gallons), but they have faster fuel consumption, and after filling, they can provide 8-12 hours under a load of 50 percent.
Inverter generators operate on a smaller fuel tank (1-4 gallon) and will have a longer working time. Most inverter models are capable of running on a single tank 8-10 hours at 25 percent load and smaller models can go up to 20 hours at the lowest load.
Load Management and Parallel Operation
Numerous inverter generators include the option of parallel operation that means two identical generators may be paired to provide higher power output. This aspect comes as an advantage since it allows the user to have flexibility in terms of power requiring a higher power when necessary but the portability and efficiency of a smaller sized unit in most other cases.
Conventional generators seldomly support parallel operation which demands consumers to physically acquire one generator based on maximum power they might frequently use and consume in case consummation of such power is only occasional.
Size, Weight, and Portability Factors

Physical Dimensions and Weight
One of the major strengths of inverter generators is its portability. High engineering and miniaturization of components has enabled the manufacture of inverter units capable of fitting more power with less weight and size. A 3000 watt inverter generator may measure 55-65 pounds against 80-100 pounds in the case of a similar capacity conventional old generator.
This weight difference is significant to the customers who require portability in carrying their generators around like construction contractors, RV enthusiasts or people who keep their generators in their garages or basements.

Storage and Transportation
Due to the size, inverter generators are easier to store in cars, RVs or the small storage area. Most of the models come in built-in wheels and handles to ensure ease of transportation. They also occupy less room when storing them and that can be helpful when preventing theft.
Bulky and heavier generators A conventional generator may necessitate designated storage facilities as well as the provision of ramps or hoists to handle the load when transporting generators by truck or other vehicles.
Environmental Impact and Emissions
Fuel Consumption and Carbon Footprint
Use of generator has nature environmental effects which highly relies on consumption and emission levels. The high fuel efficiency of inverter generators is directly proportional to its carbon footprint and the environment. The 40 percent fuel savings translates to 40 percent lesser amount of emissions every hour of utilization.
Emissions Standards and Regulations
The two types of generators need to comply with the emission standards set by EPA and CARB but inverter generators often exceed these standards because efficient combustion and electronic engine burn-management tools are always present. There are regions where there is tight control on emissions and this favors clean burning machines.
Noise Pollution Considerations
The lower sound level given by inverter generators is part and parcel of environmental friendliness due to the noise pollution that occurs. This is especially significant when used in residential premises, camp sites or other places where there are constraints of noise pollution.
Best Use Cases for Each Generator Type

When to Choose Traditional Generators
Conventional generators have been successful in cases where capacity of maximum output power is the major requirement and the cost factor is very crucial. They are perfect in:
- A construction site which needs high-power tools
- Back up power–whole house–transfer switches
- Emergencies in which the first cost determines it all
- Applications in which noise levels are not of main concern
- Users familiar with elementary maintenance of mechanics
When to Choose Inverter Generators
Applications where efficiency in fuel usage, acoustical performance, and environmentally friendly power output are of the highest priorities use inverter generators:
- Leisure activities such as camping and tailgating
- Running delicate medical and electrical gear
- Power outages that involve restrictions on travel and it is important to save on fuel
- Noise-constricted residential places
- Programs that need transport a lot
Maintenance Requirements and Longevity
Routine Maintenance Needs
Both the types of generators need servicing such as oil change, air filter, and spark plug as well as fuel system all these are required periodically. Conventional generators suffer all in favor of an easier accessibility of the service points and easier routine maintenance.
The complex electronic systems that are needed in inverter generators may have to be maintained more often, but the ability to run the engine at variable speeds (reducing wear by running at lower speeds when lightly loaded) can increase the overall lifetime possible.
Long-Term Reliability
Both the types of generators need servicing such as oil change, air filter, and spark plug as well as fuel system all these are required periodically. Conventional generators suffer all in favor of an easier accessibility of the service points and easier routine maintenance.
The complex electronic systems that are needed in inverter generators may have to be maintained more often, but the ability to run the engine at variable speeds (reducing wear by running at lower speeds when lightly loaded) can increase the overall lifetime possible.
Future Trends and Technology Developments
Emerging Technologies
The generator market industry is developing and improving with batteries technology, pulling in solar, and smart connectivity. The hybrid systems which incorporate the traditional engines with a battery storage are on the rise, bringing the advantages of both systems.
Market Trends
Environmental awareness on the one hand and the lessening of noise limits on the other hand are making consumer choices favor quieter, more efficient generators. The trend is inclined towards inverting technology even though the initial costs are higher.
Conclusion
The decision between the traditional generators and inverter generators is based on your individual needs, financial extent and usage. Traditional generators are the most powerful and have the lowest initial cost hence are best in heavy duty usage and cost conscious customers. The inverter generators are more fuel efficient, less noisy and cleaner regarding power delivery, suited best to their recreational use, sensitive electronics and environmentally friendly consumers.
Best decision: take into consideration a power consumption, the frequency of using it, the tolerance of noise, and your budget. Although the initial investment in inverter generators is more, they can be effective to use in many applications because the operational advantages compensate the invested money in the generator in cases when the user is concerned with efficiency, noise reduction and clean power supply.