
Introduction
A 9-volt battery is a small power source extensively used in industrial and household settings. Common in devices needing a consistent power source, this battery is easily identified by its rectangular form and snap-style connectors. The 9-volt battery offers portable and effective power whether in smoke detectors, radios, medical equipment, or electronic tools.
The structure, features, varieties, uses, pros and cons, and maintenance advice for 9-volt batteries are investigated in this page. Keep reading for an in-depth study to help you to grasp what makes these batteries indispensable.
Structure and Composition of a 9-Volt Battery
Six smaller 1.5-volt cells coupled in series form a 9-volt battery. Usually stacked inside the rectangular casing, these cells enable the small design characteristic of this battery type.
Components Inside a 9-Volt Battery

- Often composed of zinc or another reactive metal, anode (negative terminal) is
- Usually made of manganese oxide, carbon, or other materials depending on the type of battery, the cathode—positive terminal
- An electrolyte is a chemical agent allowing ion flow between electrodes to create electricity.
- Usually made of metal or plastic, casing shields the internal parts from outside conditions.
Types of 9-Volt Batteries

Each of the several variants of the 9-volt battery is appropriate for a different use. Knowing the variations will enable you to choose the correct one for your requirements.
1. Alkaline 9-Volt Battery
- Most often found in domestic electronics.
- produces a steady voltage output.
- Comparatively to lithium substitutes, modest lifetime.
- Usually throwaway, although some rechargeable models are available.
2. Lithium 9-Volt Battery
- extends battery life above that of alkaline models.
- does nicely in very high or low temperatures.
- Perfect for highly drain devices like smoke detectors.
- Not rechargeable but lasts noticeably longer than other kinds.
3. Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) 9-Volt Battery
- rechargeable and ecologically benign.
- Low voltage output relative to alkaline or lithium.
- Perfect for daily use products including remote controls and wireless microphones.
4. Nickel-Cadmium (NiCd) 9-Volt Battery
- Rechargeable but influenced by memory effect; needs complete discharge before recharging.
- Less often used because of cadmium’s environmental problems.
- Still quite valuable for some industrial uses.
5. Zinc-Carbon 9-Volt Battery
- a low-cost choice.
- Designed for low-power uses most appropriately.
- Less lifetime than that of alkaline or lithium.
Comprehensive Guide to 9V Battery Specifications, Equivalents, Lifespan, and Applications
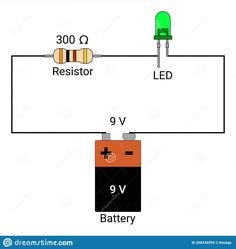
Technical Specifications of the 9V Battery
Offering a standard nominal voltage of 9 volts, the 9V battery is a commonly used power source in many different electronic devices. Different chemical compositions of the battery affect its capacity:
| Battery Type | Typical Capacity |
| Alkaline | Approximately 550 mAh |
| Carbon-Zinc | Approximately 400 mAh |
| Lithium Primary | Approximately 1200 mAh |
| Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) | Ranges between 175-300 mAh |
Furthermore fit for a range of surroundings is the 9V battery, which runs within 0°C to 60°C. Dimensions wise, for example it usually measures:
- Length: 17.5 millimetre
- Dimensions: 48.5 mm
- 26.5mm width
Alkaline, lithium, carbon-zinc, nickel-cadmium (NiCd), nickel-metal hydroxide (NiMH), and lithium-ion are among the several chemical compositions used in manufacturing of the battery that affect its performance, capacity, and lifetime.
Equivalent Batteries to 9V
Originally developed as part of the EverReady Power Pack (PP) range d batteries, the most often used variant of the 9V battery is PP3 battery. Modern industry names and codes for this standard 9V battery include:
- 6LR61
- 006P
- Duracell MN1604
- Rayovac A1604
- Energizer 522
- Varta 4922
- MX2400
- 1604A
- Radio Battery
- Smoke Alarm Battery
- 9V Block
- Krona
These several names refer to the same overall 9V battery size rated capacity and configuration, thus they can be used alternatively depending on manufacturer branding.

Lifespan and Durability of a 9V Battery
A 9V battery’s lifespan is determined in great part by its chemical composition, storage and discharge current, environment, and type of device it drives. An alkaline 9V battery’s shelf life under ideal conditions might run up to 10 years. Still, the real service life when used differs greatly:
- Devices with low energy consumption—like remote controls or smoke detectors—can run a premium 9V battery for up to five years.
- In High- Energy Applications: Battery life is drastically shortened in more power-intensive devices including portable audio equipment or walkie-talkies or mobile phones.
- Environmental Conditions: As these factors speed battery degradation, exposure to too much heat, moisture, or frequent heavy loads can shorten lifespan.
Common Uses of the 9V Battery

Because of its dependability and small scale, the 9V battery is a basic power source for a great variety of uses. Among its most often used purposes are:
- Among the most often used devices ensuring fire safety are smoke alarms.
- Radios: Designed for entertainment and communication, portable radios
- Wall clocks enable different clock designs to keep time.
- Walkie-talkies offer portable communication solutions.
- Powers portable electronic devices including test instruments, wireless microphones, and guitar pedals.
- DIY and Improvised Uses: 9V batteries have been used in unusual circumstances to generate emergency ignition sources, such as steel wool-based cigarette lighting. Such behaviors are strongly discouraged and can be dangerous, though.

The 9V battery’s adaptability makes it an indispensable part of both standard household appliances and specialized technical tools.
Rechargeable 9V Batteries and Their Variations
Two main primary size configurations for rechargeable 9V batteries are PP3 and PP9. These variances in battery capacity allow users to select a battery with a suitable charge capacity for their particular need by allowing different power demand. Among the most robust and long-lasting rechargeable 9V batteries are those of the Ansmann 9V E Type 300mAh NiMH LSD and the VARTA Ready 2 Use 200mAh 9V Ni-MH Battery.

Rechargeable 9V batteries are produced in great variety by several well-known brands including Energizer, Eneloop, Power, and Tenergy. Many of these companies provide battery packs with dedicated chargers, which helps customers to effectively maintain their batteries. While some rechargeable batteries are sold in store-bundled packages including the suitable chargers, others are often sold in blister packs including one or more cells.

Manufacturers, vendors, and wholesalers also provide bulk buying choices for those needing more of a supply. Often discounted, these bulk packs typically are a reasonably priced option for companies or people who regularly use 9V batteries.
Common Applications of 9V Batteries
Because of their dependability and capacity, 9V batteries—disposable or rechargeable—are extensively used in many different sectors. Among the most often used applications are:
- Essential for systems of fire safety, smoke alarms and detectors
- Portable two-way radios include walk-through talkies and communication devices.
- Transistor radios power small, battery-operated radios.
- Applied in many electronic testing instruments are test and measuring instruments.
- Medical devices and equipment abound in monitoring tools, patient monitors, surgical lighting, and emergency beacons.
- LCD Displays & Digital Electronics powers smaller electronic devices and displays.
Beyond consumer electronics and healthcare, 9V batteries are also rather widely used in manufacturing, contracting, commercial buildings, education, and hotels. Their adaptability qualifies them as a vital power source in many technical and professional settings.
Understanding the True Voltage of a 9V Battery

Many people believe that 9V batteries always offer precisely 9 volts of power. But rather than its exact working voltage, the 9V label mostly speaks of the size and design of the battery.
- Usually offering a true 9V output, Standard Alkaline 9V Batteries
- Rechargeable 9V batteries vary in operating voltages depending on the chemistry from 6.5V to 8.4V.
- May have a nominal voltage of 7.2V, 7.4V, or 8.4V NiMH (nickel-metal hydroxide) batteries.
- Often featuring a nominal voltage of 7.2V, 8.4V, or even 9.6V, lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries
Internal cell arrangement and chemistry determine the particular voltage of discharge rate a rechargeable 9V battery.
Performance Differences Among 9V Battery Types
Not all 9V batteries work equally since the quality of their running voltage and composition define their efficiency and lifetime:
| Battery Type | Working Voltage | Performance Characteristics |
| 9.6V NiMH | 9.6V | Offers extended runtime and high power output but is relatively rare. |
| 8.4V NiMH | 8.4V | Suitable for general-purpose use but may not perform well in high-drain devices. |
| 7.2V NiMH / Lithium | 7.2V | Often made of two 3.6V cells, offering stable performance. |
| Li-ion Batteries | 3.6V – 3.7V per cell | Delivers twice the capacity of NiMH batteries. |
Usually found in two main chemistries, NiMH (nickel-metal hydride) and Lithium-Ion, rechargeable 9V batteries are
- Usually running four hours per charge, NiMH batteries
- With a 7 to 7.5 hour run-through per charge, lithium rechargeable batteries offer a noticeably longer lifetime.
Charging Considerations for Rechargeable 9V Batteries
Since most rechargeable 9V batteries are incompatible with generic battery chargers, they usually call for a specific charger. Many producers market these batteries together with a battery pack with a built-in charger.
Investing in a battery and charger combo guarantees compatibility, extends battery life, and improves battery voltage drops the general efficiency of electronic devices, so benefiting you ampere hours. Users of the advised charger can avoid possible problems with improper charging, overcharging, or underperformance.
How Does a 9-Volt Battery Work?

A 9-volt battery uses internal components’ chemical reaction to create electricity primary batteries. By means of an internal resistance external circuit, electrons migrate from the anode to the cathode when the battery is coupled to a device, so generating a flow of electrical energy to drive the device.
Different chemical reactions used in each kind of battery impact power output, lifespan, and efficiency. While lithium batteries use compounds based on lithium for greater lifetime and stability, alkaline batteries use a reaction between zinc and manganese oxide voltage rises.
Common Applications of 9-Volt Batteries

9-volt batteries find great use in many different applications because of their size and steady voltage output zener diode. Here are a few rather frequent applications:
1. Smoke Detectors
Among the most important applications for 9-volt batteries is in smoke detectors. Home safety depends on the stable battery voltage since it guarantees dependable operation in fire hazard detection.
2. Guitar Pedals
Many times, musicians use 9-volt batteries in their effects pedals. The battery guarantees continuous performance since it offers portable and pure power.
3. Walkie-Talkies
Extended operation of many communication devices, including two-way radios and walkie-talkies, depends on 9-volt batteries.
4. Medical Devices
Because of their high quality battery dependability and lifetime, devices including hearing aids and blood glucose monitors sometimes run on 9-volt batteries non rechargeable.
5. Remote Controls
Nine-volt batteries are routinely used in garage door openers, security system remotes, and other wireless controllers.
6. Portable Radios
Battery-operated radios are a great source of news and emergency information during blackouts or outside events.
Advantages of 9-Volt Batteries
Popular for their several advantages, the 9-volt battery has:
- Small and simple for fitting in portable devices, compact design
- Guarantees consistent performance from stable voltage output.
- Among the choices are disposable, rechargeable, and long-life batteries.
- Simple installation and replacement of eases of use.
- Mostly sold in hardware and electronics stores, widely available.
Disadvantages of 9-Volt Batteries
Nine-volt batteries have certain disadvantages even with their benefits:
- Restricted Capacity: Their energy storage is lower than that of more general battery kinds.
- More costly per unit of energy than either AA or AAA batteries.
- Shorter Lifespan in High-Drain Devices: Drains fast in devices needing high power.
- Environmental Issues: Discosible models add to battery waste.
Tips for Proper 9-Volt Battery Usage and Storage
These best practices will help your 9-volt battery last longer and run more efficiently:
- Store in a cool, dry environment; heat and humidity can cut battery life.
- Cover battery terminals to stop inadvertent discharge from occurring.
- Review expiry dates: Older batteries could leak or run empty.
- Recycling used batteries helps to lower environmental impact by correct disposal.
- Use the appropriate type. For dependability and long-term savings, go for lithium or rechargeable models.
Conclusion
From home safety devices to professional electronics, the 9-volt battery is a basic power source utilized in many different kinds of applications. For running many devices, its small size, steady voltage output, and great availability make it a practical and quick choice. To maximize its advantages, though, its rather low capacity and price call for careful choice and appropriate use.
