
Introduction
Found in everything from remote controls and lamps to toys, watches, and mobile electronic devices, alkaline batteries are among the most often utilized power sources worldwide. Their relative low cost, dependability, and somewhat extended shelf life help to explain their great popularity. But voltage is one of the most crucial factors of their function since it controls their capacity to run a gadget and their lifetime before requiring replacement.

Making wise decisions about which, how to use, and maintain batteries depends on an awareness of alkaline battery and voltage requirements. This all-inclusive tutorial will go over what alkaline battery voltage is, how it varies with time, how it differs from other battery kinds, and how you could maximize battery life for best performance.
What is Alkaline Battery Voltage?

An alkaline battery’s voltage is the electrical potential difference separating the cells at its positive and negative terminals. The quantity of electrical energy the battery can provide to a circuit depends on this voltage.
When new, a normal alkaline battery—like AA, AAA, C, or D—has a nominal voltage of 1.5 volts (V). Over the lifetime of the battery, this voltage does not stay constant though. The voltage of the battery steadily drops as it runs empty, which influences the power capacity of a gadget.
Why is Voltage Important?

Whether a battery can efficiently run a device depends in great part on voltage. Correct operation of primary batteries in many electronic equipment depends on a minimum voltage threshold. Should the battery voltage drop below this level, the gadget can become slow, malfunction, or completely stop running.
For example:
- A flashlight could fade as battery voltage falls.
- Weak batteries could make a remote control less sensitive.
- Even in cases when the batteries still have some life, a digital camera could turn off.
Knowing how alkaline battery voltage fluctuates with time will enable consumers to make sure their gadgets run effectively and decide when to update batteries.
Factors That Affect Alkaline Battery Voltage

The voltage output of an alkaline battery depends on several elements:
1. State of Charge
Although a completely charged alkaline battery offers roughly 1.5V, this voltage decreases as the battery runs down to 1.2 volts. The battery is said to be almost depleted whenever the voltage drops below 1.0V.
2. Current Draw (Load)
The voltage of a battery changes with the current a device draws. High-power devices like motorized toys or digital cameras draw more current, which lowers battery voltage more quickly.
3. Temperature
Battery performance depends in great part on temperature.
- Reduced voltage output of the battery results from slowed down chemical reactions within it caused by cold temperatures.
- Faster voltage loss results from increased self-discharge brought on by high temperatures.
4. Battery Age and Shelf Life
Alkaline batteries progressively lose voltage over time from internal chemical processes even in non-use. Starting voltage of a battery kept over several years could be several factors lower than that of a brand-new one.
5. Battery Quality and Brand
Not every alkaline battery is produced equal. Generally speaking, premium brands offer longer-lasting power and more steady voltage levels than less expensive substitutes.
How Alkaline Battery Voltage Changes Over Time

Alkaline batteries gradually lose voltage as they are used, unlike certain rechargeable batteries that have a constant voltage until decreasing rapidly.
- (~1.5V) fully charged state—new or fresh batteries
- Partially Discharged State: Moderately used 1.2V – 1.3V
- Near Depletion: ~1.0V or below ( Battery needs replacement)
Many electronic gadgets quit working right before the battery is empty. While some gadgets, like digital cameras, need a greater voltage to run well, some—such dead ones such as clocks and remote controls—can still run at lower voltages.
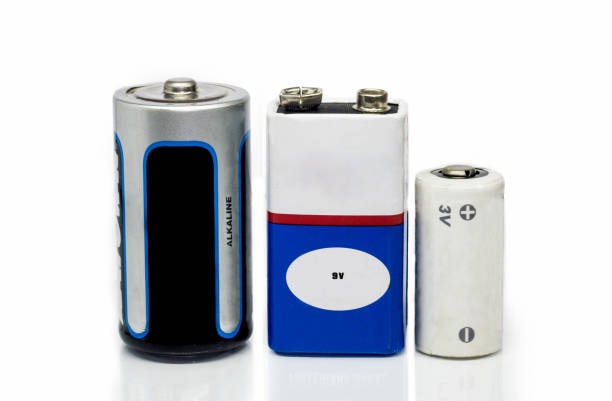
Understanding Alkaline Battery Types and Their Maximum Voltage

Among the most often utilized power sources for different electronic equipment, alkaline batteries provide dependability and long-lasting energy. Each of these batteries, which range in voltage and size, is intended for particular use. Whether your gadget is remote control, flashlight, smoke detector, or toy, selecting the correct kind of alkaline battery guarantees best performance for it.
The several kinds of alkaline batteries that are already on the market, their features, and the highest voltage they can produce when completely charged will be discussed in this paper.
Types of Alkaline Batteries

Physical size and voltage capacity define the groups of alkaline batteries. The most often used forms consist in:
1. AA Alkaline Batteries
Found in a wide range of household devices like remote controls, clocks, toys, and torches, AA batteries are the most often used alkaline battery type. Appropriate for medium-power electronics, these cylindrical batteries have a nominal voltage of 1.5V.
2. AAA Alkaline Batteries
Though smaller in size, AAA batteries are identical to AA batteries. Small flashlights, wireless mice, laser pointers, and TV remotes are just a few of the little technological gadgets they find frequent use in. Though their smaller size causes them to usually store less energy, AAA batteries have a nominal voltage of 1.5V, same as AA batteries.
3. 9V Alkaline Batteries
Rectangular in form, 9V batteries are extensively found in medical equipment, walk-through radios, and smoke detectors. 9V batteries have a nominal voltage of 9V, unlike AA and AAA batteries, which offer a lower voltage, hence they are appropriate for devices needing more power output.
4. C and D Alkaline Batteries
Larger than AA and AAA batteries, C and D batteries find application in high-drain devices including children’s toys, radios, and big flashlights. These batteries have a nominal voltage of 1.5V, same to AA and AAA batteries although their higher physical size and energy storage capacity. Their bigger scale, however, lets them provide more consistent power over a longer period.
Maximum Voltage of Alkaline Batteries

An alkaline battery’s maximum voltage is its highest voltage it can provide upon either new or completely charged state. As the battery runs down with operation, this peak voltage steadily falls. The highest voltage various kinds of alkaline batteries may produce is broken down below:
1. AA and AAA Alkaline Batteries
- Both AA and AAA batteries may offer a peak voltage of 1.6V when completely charged.
- This voltage steadily decreases over time as the battery is used until it reaches the point that the device cannot operate effectively.
2. 9V Alkaline Batteries
- Slightly higher than its nominal 9V rating, a completely charged 9V alkaline battery can offer a peak voltage of 9.6V.
- Devices dependent on constant power suffer as the battery runs down since the voltage drops.
3. C and D Alkaline Batteries
- When brand-new, C and D batteries can offer a peak voltage of 1.6V, same as AA and AAA batteries.
- These batteries have a far higher energy capacity than AA or AAA batteries because of their size, which lets them run equipment for longer lengths of time.
Alkaline Battery Voltage vs. Other Battery Types
One should know how alkaline battery voltage stands in relation end voltage and to different battery chemistries:

- For some high-drain devices, nickel-metal hydroxide (NiMH) Rechargeable Batteries are preferable even if their nominal voltage (1.2V) is lower. Their constant output across their discharge cycle makes all the difference.
- Usually with a far higher voltage of 3.7V per cell, lithium-ion batteries are incompatible with most appliances built for alkaline batteries.
- Though usually with less capacity and less consistent voltage, zinc-carbon batteries resemble alkaline batteries.
Minimum Voltage of Alkaline Batteries

An alkaline battery’s minimum voltage is the point at which the voltage falls so low the battery cannot supply enough power to run a device. Though it may still have a minor residual charge, at this point the battery is usually regarded as “dead”. Typical minimum voltage levels for several kinds of alkaline batteries are shown below:
1. AA and AAA Alkaline Batteries
- Minimum voltage: About 0.9V.
- Most electronic devices will not run as intended once the voltage of an AA or AAA battery falls below 0.9V.
- Some low-power gadgets, like basic LED torches or clocks, might run for a brief while but performance will be greatly compromised.
2. 9V Alkaline Batteries
- Minimum Voltage: Around 6V
- A 9V alkaline battery is said to be exhausted when its voltage drops to 6V or below.
- Many equipment, such wireless microphones and smoke detectors, call for a steady voltage source. These devices can begin to provide low-battery warnings or stop working completely once the battery falls below this level.
3. C and D Alkaline Batteries
- Minimum Voltage: About 0.9V, same to AAA and AA batteries
- Though they physically are bigger and have more energy capacity than AA and AAA batteries, C and D batteries nevertheless follow the same voltage discharge pattern.
- Their voltage will drop below 0.9V and they will no longer be able to efficiently run motorized toys or portable radios, among high-drain gadgets.
Alkaline Battery Voltage Curve
An alkaline battery’s voltage curve shows how its voltage varies with progressive discharge. Estimating not rechargeable battery for life and guessing when a device might stop working depend on an awareness of this curve.
Characteristics of the Alkaline Battery Voltage Curve
1. Initial Voltage Drop
- Brand-new or fully charged an alkaline battery offers a peak voltage of 1.6V (for AA, AAA, C, and D batteries) or 9.6V (for 9V batteries).
- Usually in the first few hours of operation, there is a minor initial reduction in voltage as soon as the battery starts to be utilized. Still, most devices’ performance is not much impacted by this decline.
2. Stable Voltage Period
- For most of the lifetime of the battery, the voltage stays somewhat constant following the initial dip.
- The battery keeps effectively running devices during this phase, hence consumers might not find any performance drop.
- The power usage of the device and the battery quality determine this stability period.
3. Gradual Voltage Decline
- The voltage gradually lowers as the battery approaches the final phases of its life.
- Devices might start to show symptoms include dimmer lights, slower running speed, or lesser audio output.
- At this point several electronic devices could show a low battery warning.
4. Rapid Voltage Drop (End of Life)
- The voltage of a battery starts to rapidly decline once it hits a critical discharge threshold.
- Devices needing a constant voltage will start to fail or shut down.
- While for 9V batteries this quick drop occurs near 6V, for AA, AAA, C, and D batteries it occurs around 0.9V to 1.0V.
- The battery needs to be replaced since at this point it is practically dead.
How to Measure Alkaline Battery Voltage
Using a digital multimeter and these guidelines will help you to check the voltage of an alkaline battery:
- Most multimeters offer a DC voltage (V) setting that lets one test batteries. Set the multimeter to DC voltage mode.
- Touch the black probe to the negative(-)-terminal and the red probe to the positive (+) terminal.
- Look at the voltage display.
- A value of 1.5V or above indicates complete battery charge.
- A measurement of 1.2V – 1.3V points to moderate use.
- A value less than 1.0V suggests almost complete depletion of the battery.
How to Maximize Alkaline Battery Voltage and Lifespan
Think about these excellent ideas to maximize your alkaline batteries:
1. Store Batteries Properly
- Store batteries cold, dry to reduce voltage loss.
- Stow batteries away from excessive heat or cold to prevent performance degradation.
2. Use Batteries in Matching Sets
- Use batteries of the same brand, age, and charge level whenever utilizing many batteries in a gadget to avoid unequal discharge.
3. Turn Off Devices When Not in Use
- Many devices run even in standby mode, gradually draining battery voltage.
4. Choose the Right Battery for the Job
- Using lithium or rechargeable NiMH batteries instead of alkaline ones improves performance of high-drain devices (such as digital cameras, high-power torches).
5. Remove Batteries from Unused Devices
- Eliminating the batteries will stop sluggish discharge and leakage should a device not be used for a long period.
How to Check the Voltage of Alkaline Batteries
An efficient approach to make sure alkaline batteries still have enough charge to run your equipment is routinely verifying their voltage. A battery that has dropped below a specified voltage level could no longer run effectively, which would cause problems with the operation of electrical gadgets. Testing the voltage helps you ascertain whether a battery needs to be replaced or whether it is still useable.
An alkaline battery’s voltage can be checked primarily using a multimeter or a battery tester. Both techniques are easy and will help you evaluate the state of your batteries before they run totally empty.
Method 1: Checking Voltage Using a Multimeter
Widely used electrical instrument capable of measuring voltage, current, and resistance is a multimeter. Examining the voltage of an alkaline battery is among the most consistent methods available. Use these guidelines to precisely gauges the voltage of the battery:
Step 1: Set the Multimeter to DC Voltage Mode
- Since most alkaline batteries run on direct current (DC), it is advised to set the multimeter to DC voltage mode (typically indicated as “V” with a straight line and dashed line under).
- Choose the multimeter’s one closest to the predicted voltage (e.g., 2V or 20V for AA/AAA/C/D batteries, and 20V for a 9V battery) if the multimeter features several voltage ranges.
Step 2: Position the Multimeter Probes Correctly
- Identify the battery terminals: The positive terminal is usually marked with a (+) sign, while the negative terminal is marked with a (-) sign.
- Connect the probes:
- Place the red probe on the positive (+) terminal of the battery.
- Place the black probe on the negative (-) terminal of the battery.
Step 3: Read the Multimeter Display
- Find the battery terminals: Usually indicated by a (+) sign, the positive terminal is found; the negative terminal is indicated by a (-).
- Interpret the reading depending on the kind of battery:
- AA, AAA, C, and D Batteries:
- A value of 1.5V or more indicates good battery status.
- A result below 1.0V suggests that the battery should be almost totally exhausted and replaced.
- 9V Batteries:
- Reading 9V or above indicates that the battery is in good running order.
- A value below 6V points to a poor battery that might not run most gadgets successfully.
- AA, AAA, C, and D Batteries:
Method 2: Checking Voltage Using a Battery Tester
A basic and cheap tool meant especially to measure battery voltage is a battery tester. Unlike a multimeter, which calls for manual setup, a battery tester offers a rapid and simple approach to verify battery life rechargeable aa batteries.
How to Use a Battery Tester:
- On the battery tester, place the alkaline battery in the allocated slot.
- Make that the battery’s positive and negative terminals match the contacts of the tester exactly portable electronics.
- Usually color-coded, the battery tester will show the voltage reading:
- The battery is in a green zone—that is, it is still useable and sufficiently charged.
- Yellow zone: The battery might soon need replacement as it is deteriorating battery’s flat.
- Red zone: The battery has to be replaced right away since it is dead.
Common Myths About Alkaline Battery Voltage
1.”Alkaline batteries always have stable voltage output at a consistent 1.5V.”
- False. Starting at 1.5V, their voltage falls steadily as they discharge.
2. Refrigerating alkaline batteries increases their lifetime.
- Partially true. Although low temperatures slow down chemical reactions, refrigeration’s dampness can harm batteries. Better still is a cool, dry place of storage.
3.”Freezing a dead alkaline battery will help you to revive it.”
- False. Although freezing a dead battery may somewhat restore weak voltage, the capacity of the battery stays low.
Conclusion
The performance of a battery over time depends much on its alkaline battery voltage. Although alkaline batteries begin with a nominal value of 1.5V, as they deplete their voltage steadily falls. Their performance can vary depending on temperature, current draw, and storage conditions among other elements. Users can guarantee they get optimum efficiency and lifetime from their batteries by correctly storing them, using them in compatible devices, and using proper voltage and measuring when needed. For a range of electronic equipment nickel metal hydride, alkaline batteries offer a consistent and dependable power source; nevertheless, as they deplete over time their voltage naturally drops. While for 9V batteries it is roughly 6V, the lowest voltage for AA, AAA, C, and D batteries is about 0.9V. Most gadgets cannot be efficiently powered from a battery after the voltage falls below certain thresholds alkaline cells.
An alkaline battery’s voltage curve is predictable: an initial decrease soon after first use, a steady period whereby the voltage is somewhat constant, a slow fall, and lastly a fast voltage drop at the end of its life. Understanding how alkaline batteries’ discharge curve over time helps users to predict when a battery replacement is required and guarantees that their gadgets will keep running as best they could.
Summary
Usually having a nominal voltage of 1.5V, alkaline batteries eventually lose this as the battery runs down. Voltage levels and general performance are influenced by things including current draw, temperature, and battery age. A multimeter’s measurement of battery voltage might assist one ascertain when a battery requires replacement. Proper storage, use in matched sets, and removal from unneeded equipment help to increase aa alkaline battery voltage and life. Although low-to-moderate power gadgets benefit from alkaline batteries, high-drain electronics may run better on NiMH or lithium batteries replace battery. Understanding the workings of alkaline battery voltage helps consumers make wise decisions to increase gadget performance and efficiency exact voltage.

