
One of the most often used kind of batteries worldwide, AA batteries run anything from cameras and toys to remote controls and spotlights. One of the most crucial factors to consider while buying AA batteries is their milliampere-hour (mAh) rating. This figure shows the capacity of the battery and is therefore very important for the running time of a gadget before it requires fresh batteries or a recharge.

Everything about AA battery mAh will be covered in this extensive tutorial, including several battery kinds, their mAH capacity, how to choose the correct battery, and advice on extending battery life.
What Is mAh and Why Does It Matter?

A battery’s mAh (milliampere-hour) value indicates its capacity—that is, its capacity to store and deliver over time the electrical charge. It gauges a battery’s capacity to provide a given length of time before it is completely depleted.
A battery rated at 1800mAh, for example, can provide maximum current of 18mA (milliamperes) for 100 hours, or alternatively 180mA for 10 hours before running low. Assuming constant power use for the gadget, the battery will last longer the larger the mAh rating.

But when you compare several kinds of batteries—such as NiMH, or alkaline cells, or lithium—you must assess them under the same discharge settings. Different battery chemistries perform differently under different loads, hence the comparisons might not be accurate otherwise.
NiMH vs. Alkaline AA Batteries: How Do Their mAh Ratings Compare?

You could find NiMH rechargeable AA batteries and alkaline disposable AA batteries while looking for AA batteries. Although both may run the same gadget, their capacity ratings (mAh values) vary greatly even if their performance is equal.
NiMH (Nickel-Metal Hydride) AA Batteries

- Common Capacity Range: 1200mAh to 2500mAh
- Rechargeable: yes
- Perfect for high-power, often used electronics such digital cameras, gaming consoles, and electric toothbrushes.
Measuring under defined charge and discharge settings, most NiMH AA batteries purchased in stores have capacity ratings between 1200mAh and 2500mAh. A 2500mAh NiMH battery, for instance, will supply 2500mAh of useful power when charged and discharged at 0.2C with a discharge cutoff voltage of 1.0V.
Alkaline AA Batteries

- Typical Capacity Range: varies greatly depending on discharge circumstances ( 650mAh to 3150mAh).
- Rechargeable: Not present
- Perfect for low-power needs including wall clocks, remote controls, and flashlights.

Unlike NiMH batteries, alkaline batteries hardly ever have their capacity (mAh) or exact capacity stated on the box. This is so because alkaline batteries work differently—they transform chemical energy into electrical energy by a non-rechargeable process. Furthermore, their capacity changes based on the particular device they are used on and the rate of discharge. It is not a fixed figure.
Key Differences in Performance Between NiMH and Alkaline Batteries

- Marked Capacity (mAh Labeling)
- Clearly indicated m Ah rating of NiMH batteries reflects their useable capacity under normal discharge circumstances.
- Because their capacity varies depending on the electrical load and discharge rate, alkaline batteries lack a clearly stated mAh rating on their packaging.
- Usability in High-Drain Devices
- Because NiMH batteries can run a constant current until exhaustion, they are more suited for high-power equipment (such as cameras and electric toothbrushes).
- Because their capacity is maximized when discharged slowly over time, alkaline batteries perform best in low-power devices (such as TV remotes and clocks).
- Actual Capacity Differences Under Load
- In a high-power gadget, a 2500mAh NiMH battery will essentially be fully charged.
- Placed in the same high-power gadget, a 2500mAh alkaline battery might not provide its entire advertised capacity and will degrade far more quickly.

For an electric toothbrush (a high-power item), for instance, a 2500mAh NiMH battery will last noticeably more than a 2500mAh alkaline cell. This is so because NiMH batteries more effectively manage high current draw full-power loads than alkaline batteries, which lose a lot of capacity under high current demands.
Alkaline AA Battery Capacity Under Different Discharge Conditions

Since alkaline battery capacity is influenced by the discharge rate, different testing conditions yield varying mAh values. Here are some real-world examples:
- 2250mAh when discharged at 3.9Ω, 1h/h, down to 0.8V
- 1900mAh when discharged at 3.9Ω, 24h/h, down to 0.9V
- 3150mAh when discharged at 24Ω, 25s/m, 8h/h, down to 1.0V
- 2600mAh when discharged at 43Ω, 4h/h, down to 0.9V
- 650mAh when discharged at 50mA, 1h/8h, 24h/d, down to 1.0V
- 2000mAh when discharged at 250mA, 1h/d, down to 0.9V

These values show that in low-drain applications—where they can release their full capacity over time—alkaline batteries perform better. In high-drain devices, their real capacity can be much less than their theoretical mAh rating, nevertheless.
What Should You Consider Besides Capacity (mAh) When Buying Batteries?

Particularly with alkaline batteries, it’s crucial to consider factors other than mAh rating when buying batteries. Here are some salient features to consider:
1. Rechargeability vs. Disposable Usage
- Should your gadget call for regular battery changes, NiMH rechargeable batteries are a reasonably priced and ecologically beneficial option.
- Given their lengthy shelf life, alkaline batteries could be a better choice if your gadget is used seldom.
2. Device Power Requirements
- NiMH or lithium batteries are advised for high-power gadgets such digital cameras, game consoles, and electric toothbrushes.
- Alkaline batteries perform best for low-power devices including wall clocks and TV remotes.
3. Alkaline Battery Marketing Labels
- Terms like “Plus Alkaline” or “Ultra Alkaline” often used in alkaline batteries imply they last longer than regular alkaline batteries. Though they may have longer runtimes, these premium models usually cost more.
What Does mAh Mean in AA Batteries?

A battery’s mAh (milliampere-hour) value gauges its capacity for storing energy. It shows the battery’s capacity for charge over time. Simply said, the battery may survive longer before running empty the higher its m Ah.
For example:
- Before being totally depleted, a 2500mAh AA battery can supply 2500mA (2.5A) for one hour or 1250mA for two hours.
- Before depletion, a 1000mAh AA battery will run 500mA for two hours or 1000mA for one hour.

Choosing batteries for various devices depends on an understanding of this rating since choosing the wrong type could result in poor performance and frequent replacements.
Different Types of AA Batteries and Their mAh Ratings

varied m Ah capacity and appropriate for varied uses define the several kinds of AA batteries available. The most often used AA batteries are broken out here:
1. Alkaline AA Batteries

- Capacity: 2000 to 3000mAh
- Designed for low-drain devices including LED torches, clocks, and remote controls.
- Benefits include widely available, reasonably priced, non-charging requirements.
- Cons: reduced efficiency in devices with high drain, non-rechargeable.
2. Lithium AA Batteries
- Capacity: About 3000MHV
- Perfect for high-drain devices including digital cameras, medical tools, GPS systems, and smoke detectors.
- Longer lifespan, lightweight design, and performance in very hot environments are advantages.
- Cons: Non-rechargeable and more costly.
3. NiMH (Nickel-Metal Hydride) Rechargeable AA Batteries
- Capacity: Usually 600 to 2800mAh
- Perfect for often used tools such torches, wireless keyboards, and gaming controllers.
- Rechargeable, reasonably priced over time, and ecologically friendly among other benefits duty cycle.
- Cons: Needs a charger; loses charge over time while kept.
4. NiCd (Nickel-Cadmium) AA Batteries
- Capacity: 600 to 1000 volts
- Perfect for industrial uses and older devices.
- High discharge rate makes sense for high-drain devices.
- Cons: Contains poisonous cadmium; has memory effect; less capacity than NiMH larger cells.
How to Choose the Right AA Battery Based on mAh

The power consumption of your device and how often you use it will determine the suitable AA battery for it. The following guides help you choose the ideal battery:

1. For Low-Drain Devices
- Not requiring a large energy output, devices include remote controls, clocks, and smoke detectors perform effectively with alkaline AA batteries (1000–3000mAh).
2. For High-Drain Devices
- NiMH rechargeable AA batteries (2000–2800mAh) or lithium AA batteries (3000mAh) for longer-lasting power help digital cameras, gaming controllers, and strong spotlights.
3. For Frequent Use Devices
- High-capacity NiMH rechargeable AA batteries (2500–2800mAh) give superior cost effectiveness and over time help to lower waste if your gadget is used everyday aa alkaline batteries.
4. For Extreme Conditions
- Because of its extened shelf life and durability, lithium AA batteries (3000mAh) are perfect for long-term storage and high temperatures ni mh.
Technical Specifications of AA Batteries (Alkaline, Lithium, and Carbon Zinc)
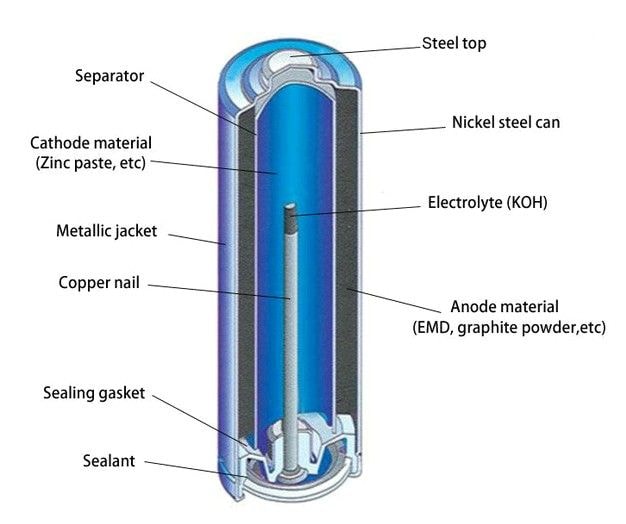
Each of the several chemical compositions of AA batteries has special properties that affect their voltage, capacity, and performance same voltage
. Alkaline, lithium, and carbon zinc AA batteries—the three most often used varieties—diffiate in energy storage, lifetime, and best use scenarios. Based on their features, the table below offers a thorough comparison of several battery kinds.
| Battery Type | Nominal Voltage | Average Capacity (mAh) | Operating Temperature Range | Diameter | Height | Chemical Composition |
| Alkaline AA Battery | 1.50 Volts | ≈ 2500mAh | 0°C – 60°C | 14.5mm | 50.5mm | Alkaline |
| Lithium AA Battery | 1.50 Volts | ≈ 3000mAh | 0°C – 60°C | 14.5mm | 50.5mm | Lithium |
| Carbon Zinc AA Battery | 1.50 Volts | ≈ 400-1700mAh | 0°C – 60°C | 14.5mm | 50.5mm | Carbon Zinc |
Key Takeaways from the Specifications
- Voltage Consistency
- For most typical AA battery uses, all three battery types—Alkaline primary batteries, Lithium, and Carbon Zinc—have a nominal voltage of 1.50 volts and are therefore interchangeable.
- Capacity Differences
- With an average capacity of around 3000mAh, lithium AA batteries let high-drain devices run for longer 1.5 v.
- With ≈2500mAh, alkaline AA batteries are a dependable and generally accessible option for daily devices.
- With a capacity ranging between 400mAh and 1700mAh, Carbon Zinc AA batteries are more suited for low-drain uses such remote controls and clocks constant resistance load..
- Operating Temperature Range
- Effective operation within a temperature range of 0°C to 60°C guarantees reliable performance in most indoor and outdoor environments among all three battery kinds.
- Size and Compatibility
- Since all AA batteries have the same standard measurements—14.5mm in diameter and 50.5mm in height—they can be used in devices intended for AA-sized batteries interchangeably one aa battery.
- Chemical Composition and Suitability
- Common for residential use generally are alkaline batteries.
- For high-power uses including digital cameras and medical equipment, lithium batteries are perfect because of their better performance and longer shelf life cell voltage.
- Because of their less energy storage capacity, carbon zinc batteries are ideal for low-drain applications battery industry.
Knowing the variations in capacity, chemical composition, and application compatibility helps customers choose the correct AA battery for their purpose more wisely aa cell.
Factors That Affect AA Battery Life and Performance

A battery’s lifetime and efficiency can be influenced by various external elements even if its m Ah rating is high aaa cells:
1. Device Power Consumption
- Batteries run faster in high-drain devices than in low-drain ones. A digital camera, for instance, runs batteries faster than a wall clock open circuit voltage.
2. Battery Chemistry
- Because of their steady voltage output, lithium batteries usually last more than alkaline and NiMH batteries how many mah.
3. Temperature Sensitivity
- While too much heat can harm rechargeable battery cells and cut their lifetime, extreme cold lowers battery efficiency.
4. Battery Age and Storage Conditions
- Even non-used batteries lose capacity with time, particularly in hot or humid conditions.
5. Charging and Usage Cycles (For Rechargeable Batteries)
- Recharge cycles of NiMH and NiCd batteries are few. Either overcharging or letting them discharge entirely can limit their lifetime.
AA Battery Equivalents: Different Names for the Same Size

Although the conventional AA battery is known by all, several manufacturers and brands may label them using other names. These differences in labeling have no effect on the size, voltage, or compatibility of the battery; so, they can be used alternately.
Common Equivalent Names for AA Batteries

These are some direct replacements of AA batteries depending on manufacturer-specific labeling:
- LR06, LR6, LR6A
- Duracell MN1500
- R06P, SUM4, HP7
- Varta 4106, Varta 4006
- Kodak KAA, K6A
- Toshiba LR6N
- BA3058/U
- NEDA 15A, 15AC
- Rayovac 815
- Panasonic AM3
- Energizer E91
These batteries, whatever their designation, work exactly like ordinary AA batteries. The primary variations are in manufacturer-specific identifiers and branding.
Common Uses for AA Batteries
Among the most often used battery kinds worldwide, AA batteries run many different electrical equipment. Their small yet strong nature qualifies them for both low- and high-drain uses. These are some typical applications for AA batteries:
- Digital Thermometers
- Mathematical Tools for Scientists
- Laser Point References
- Lighting Flashboards
- Panel of Control for Security Systems
- Games and Devices for Electronic Learning
- Detectors for Smoking
- Instruments and Tools for Medical Devices
- System for Memory Backup
- Rechargeable Applications: Battery Packs
For many tiny electronic devices used in homes, offices, and businesses all over, AA batteries remain the preferred power source because their adaptability.
Different AA Battery Compositions and Their Suitability
Among the several chemical compositions of AA batteries are carbon zinc, alkaline, lithium, nickel-metal hydride (NiMH), and Although most of these battery kinds are compatible in devices running AA batteries, their performance, lifetime, and discharge rates differ greatly.
Before choosing an other battery chemistry, it is always advised to consult the owner’s handbook of your device to guarantee best performance.
How to Properly Install AA Batteries in Your Device

Use these carefully to guarantee the right installation and best performance of one amp your AA batteries:
1. Identify the Positive and Negative Terminals
- On a standard alkaline AA battery, the flat side is typically the positive (+) terminal.
- The opposite end, which has a small circular protrusion, is the negative (-) terminal.
2. Match the Battery Terminals with the Device’s Markings
- Clear marks showing where to locate the positive and negative ends of the battery abound on most battery-powered appliances.
- Before putting the AA batteries into the battery compartment, carefully line their terminals with these marks.
3. Avoid Damaging the Battery Retention Tabs
- Small steel tabs built to keep the battery in place and preserve a solid electrical connection abound on several electronic equipment.
- Never bend, break, or remove these tabs since doing so could affect the device’s or battery’s performance.
- Usually, a tab moved unintentionally out of position can be gently corrected back to its natural location.
These guidelines will help you to guarantee a safe battery connection, so optimizing the lifetime and efficiency of your AA batteries.
Where to Buy AA Batteries: Ensuring Quality and Authenticity

Because of their great demand, AA batteries are produced by several companies and sold from many stores under several brands. Not all AA batteries, nevertheless, are of the same grade, hence certain less-quality or counterfeit models might not work as expected.
Tips for Buying High-Quality AA Batteries

- Select Trusted Brands: Stay with reliable manufacturers such Duracell, Energizer, Panasonic, Rayovac, Varta, and Toshiba.
- Purchase from Reliable Retailers – To prevent fake goods, buy from reputable internet stores or approved vendors.
- Always check the expiration date to be sure you are buying new, long-lasting power cells since batteries deteriorate with time.
- Think through the power consumption of your device. Choose high-capacity lithium or NiMH rechargeable batteries instead of regular alkaline AA batteries if your gadget calls for high-drain cells.
Recommended Online Retailer
one respectable internet merchant well-known for offering a large range of premium batteries. Having worked in the battery sector for more than 25 years, they provide a wide selection of AA batteries from reputable producers guaranteed dependability and lifespan.
How to Extend the Life of AA Batteries

Use these guidelines to maximize the performance from your AA batteries and extend their lifetime:
- For your gadget, choose the correct battery type to prevent needless drain.
- To stop capacity loss, keep batteries cold and dry.
- If a device won’t be used for very long, take batteries out of it.
- With NiMH and NiCd batteries, use a quality charger to prevent overcharging.
- To increase their lifetime, recharge batteries before they run totally empty.
Understanding the capacity of AA Batteries
Measuring in milliamp hours (mAh), AA batteries’ capacity dictates how long they may run under a given load. Measuring a battery’s capacity usually entails running a steady load until the battery voltage falls to a designated level. This procedure guides the energy output of a battery until it runs empty.
For instance, the entire battery capacity can be computed as follows if an AA battery is tested by running a 250mA load until its voltage drops to 0.8 volts and this procedure takes 12 hours:
250mA×12hours=3000mAh
250mA×12hours=3000mAh
This means that a 3000mAh battery can theoretically supply:
- 30mA for 100 hours (3000mAh ÷ 30mA = 100 hours)
- 5mA for 600 hours (3000mAh ÷ 5mA = 600 hours)
Still, battery capacity is not always constant and can be affected by temperature and current load. Extreme conditions alter the reaction of different battery chemistries, which influences their efficiency rated capacity and performance.
The Impact of Temperature on AA Battery Capacity

Under several temperature settings, battery performance might vary greatly. Temperature affects battery capacity, as seen by a comparison of Energizer AA Alkaline, Energizer AA Ultimate Lithium, and Tenergy AA Premium NiMH Rechargeable batteries at normal temperature (72°F) and in a freezer (5°F) with a 245mA load.
Battery Capacity at Room Temperature vs. 5°F
| Battery Type | Capacity at Room Temperature (72°F) | Capacity at 5°F | Percentage of Room Temperature Capacity |
| Energizer AA Alkaline | 2181mAh | 728mAh | 33% |
| Energizer AA Ultimate Lithium | 3430mAh | 3332mAh | 97% |
| Tenergy AA Premium NiMH | 2577mAh | 2213mAh | 86% |
Key Observations from the Temperature Test
- Cold temperatures greatly influence alkaline batteries; the alkaline AA battery kept only 33% of its room temperature capacity at 5°F. It restored its remaining 1453mAh capacity (2181mAh – 728mAh = 1453mAh), nevertheless, when heated back to room temperature.
- The Energizer AA Ultimate Lithium battery performed remarkably well, maintaining 97% of its original capacity even at 5°F, so making it the perfect choice for adverse weather situations. Lithium batteries are least impacted by cold.
- Though somewhat less effective than lithium batteries, NiMH batteries show little impact; the Tenergy AA Premium NiMH battery kept 86% of its original capacity, thereby providing a dependable choice for chilly situations.
How Current Load Affects AA Battery Capacity
The current load used during testing determines also the capacity of alkaline AA batteries. A smaller load yields a lower capacity; a larger load at higher voltage yields a higher capacity. By comparison, NiMH and Lithium batteries keep a more constant capacity independent of the load applied.

Battery Capacity Under Different Load Conditions
| Battery Type | 100mA Load | 250mA Load | 500mA Load |
| Energizer AA Alkaline | 2608mAh | 2181mAh | 1575mAh |
| Energizer AA Ultimate Lithium | 3475mAh | 3430mAh | 3235mAh |
| Tenergy AA Premium NiMH | 2618mAh | 2577mAh | 2485mAh |
Key Observations from the Load Test
- Alkaline batteries vary greatly in capacity depending on load – The battery ran 2608mAh @ 100mA then decreased greatly to 1575mAh at 500mA. High-drain gadgets will therefore run out an alkaline battery far faster than low-drain devices.
- Lithium and NiMH batteries preserve a constant capacity throughout many loads. For high-drain uses such cameras, flashlights, and gaming controllers, lithium and NiMH batteries are more dependable than alkaline batteries since they show only minor changes in capacity.
Methods for Measuring the Remaining Battery Capacity

Finding the remaining capacity of a battery precisely without completely draining it might be difficult. Though there are various ways, some are more dependable than others..
1. Multimeter Voltage Check (Not Recommended)
- Checking the voltage of a battery using a multimeter could produce a false and partial outcome.
- When tested without a load, a battery might display 1.5V; but, once a device is turned on, the voltage rapidly drops to 0.8V and becomes useless.
2. Battery Testers with Load Simulation (Recommended for Alkaline Batteries)
- Commercial battery testers measure the resultant voltage after momentarily loading the battery for a few seconds.
- By means of a discharge graph, the voltage is compared to enable the tester to project the residual capacity.
- For alkaline batteries, this approach performs effectively since their voltage falls regularly as they deplete.
3. Built-in Battery Meters in Devices
- Certain electronic gadgets, such trail cameras and cameras, have a battery meter that approximates their remaining charge.
- These meters apply a modest load and measure the voltage response, functioning much as battery testers.
- For lithium or NiMH batteries, however, they are not always dependable since these batteries keep a constant voltage until almost drained.
Limitations of Battery Testing Methods
- Commercial testers allow one to test alkaline batteries efficiently since their voltage declines steadily as they deplete.
- Because their discharge curves remain somewhat flat, meaning their voltage does not drop appreciatively until they are virtually empty, lithium and NiMH batteries are more difficult to monitor precisely.
- A full discharge test is the most exact way to ascertain capacity, however this leaves the battery useless subsequently.
Are Higher mAh AA Batteries Always Better?

Not exactly. Although a greater mAh number usually indicates a battery would last longer, one should take into account:
- Some gadgets have voltage or current restrictions that might not fit high-mAh batteries.
- Weight and Size: Rechargeable batteries with more capacity could be very heavier.
- Though initially more expensive, high-mAh rechargeable batteries save money over time.
Conclusion
Battery life and performance depend critically on the mAh value of an AA battery. Although a longer-lasting battery results from a higher mAh rating, the kind of battery chemistry counts also. Low-drain electronics benefit most from alkaline batteries; NiMH rechargeable and lithium batteries are excellent for high-drain uses.
Choosing the correct type for your device and knowing battery capacity will help you maximize performance, lower expenses, and limit environmental effect. Though knowing the distinctions between NiMH and alkaline AA batteries is crucial for selecting the correct one, a battery’s mAh rating defines how much power it can store and provide. While alkaline batteries best in low-power applications where gradual discharge is needed, NiMH batteries offer better efficiency for high-drain devices. Furthermore, because their performance fluctuates under several discharge scenarios, alkaline batteries do not always show an exact mAh rating.
Think about the power consumption of your gadget, whether rechargeability is your top concern, and the kind of battery chemistry that would fit your requirements as you buy batteries. Choosing wisely can help you to maximize battery life, save money, and guarantee best gadget performance.
